
The illustration of ZnO preparation via precipitation and combustion
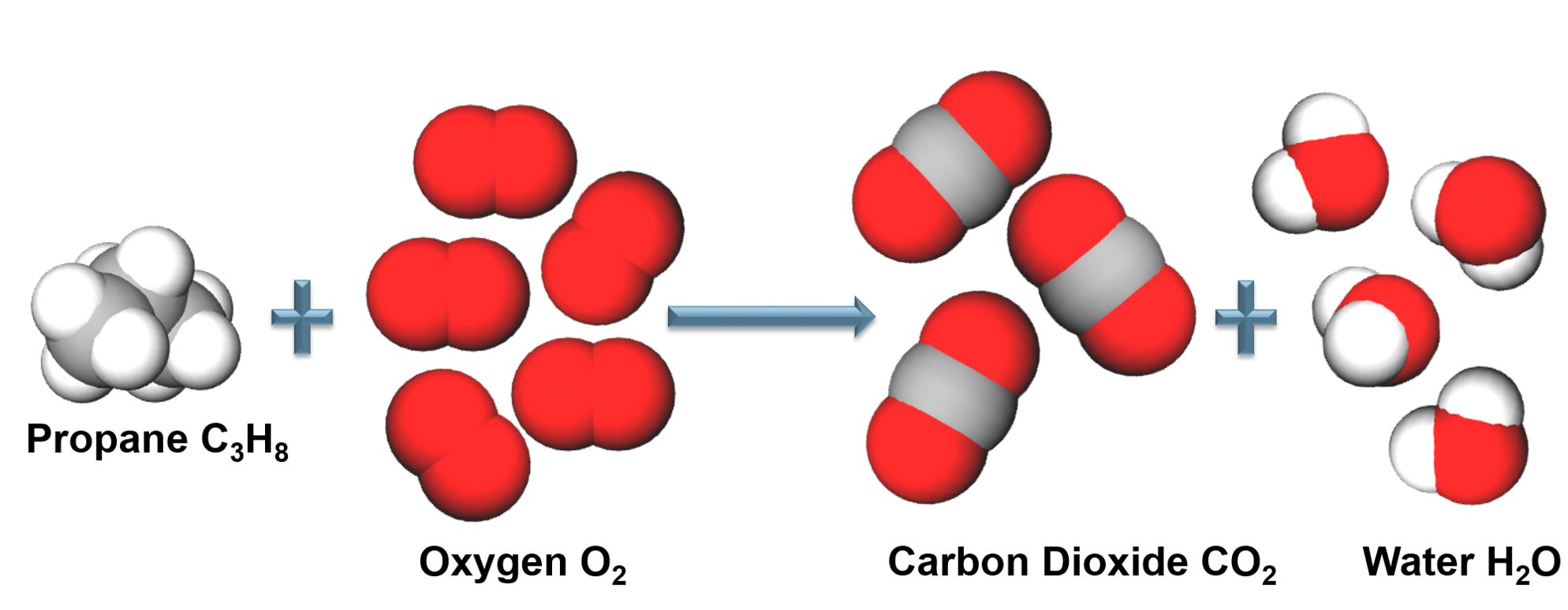
Abstract. Combustion involves chemical reactions that are often highly exothermic. Combustion systems utilize the energy of chemical compounds released during this reactive process for transportation, to generate electric power, or to provide heat for various applications. Chemistry and combustion are interlinked in several ways.
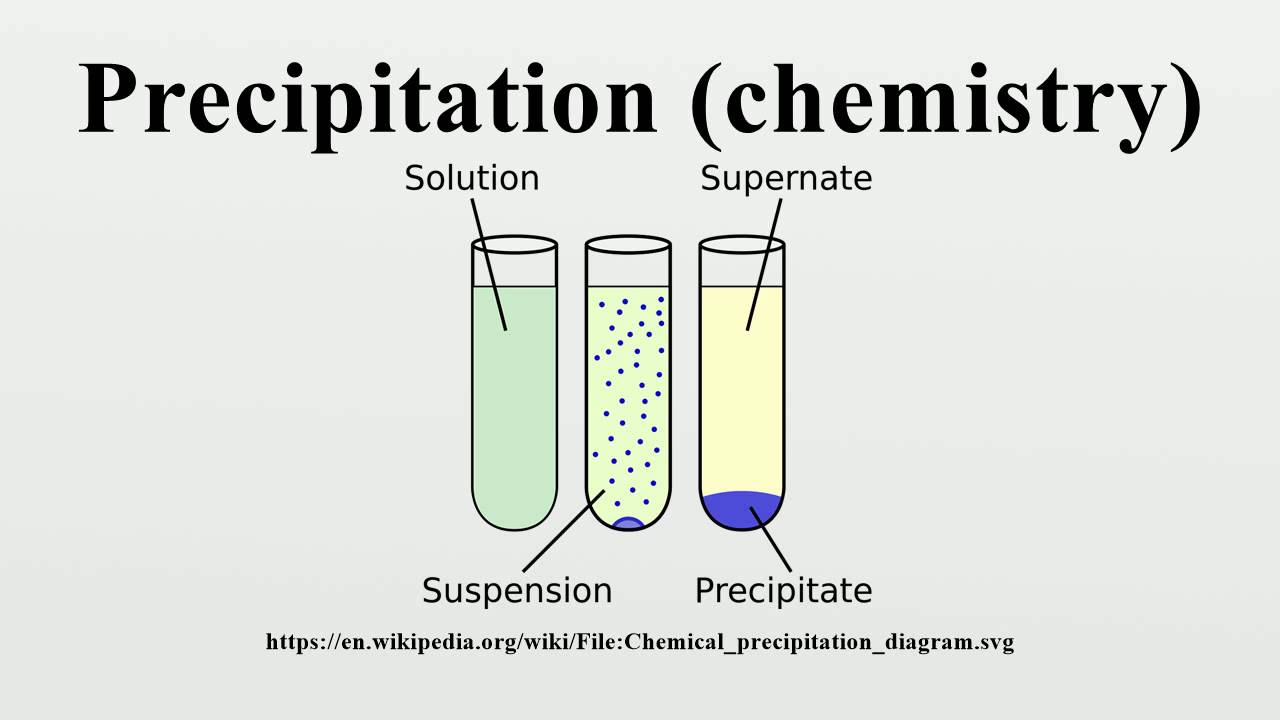
Precipitation (chemistry) YouTube
Precipitation generally refers to a relatively rapid formation of a sparingly soluble crystalline - or sometimes amorphous - solid phase from a liquid solution phase. Precipitation is rather poorly understood when compared with crystallization of more soluble materials. It generally involves the simultaneous and rapid occurrence of.

Effective removal of phosphorous from dairy wastewater by struvite
The thermodynamic driving force of precipitation in solution is described by the change in the Gibbs free energy, the difference between the chemical potential of the dissolved solute (μ 1, J mol −1) and solid (μ 2, J mol −1) (Eq. 1) [].Under constant temperature and pressure, the difference in chemical potential is expressed by the supersaturation ratio (S).

ChemicalLooping Combustion An Emerging CarbonCapture Technology
Exercise 15.3a. From the options provided, identify the salts that will form a precipitate in aqueous solution at 25 degrees Celsius. Source: "Exercise 15.3a" created by Jackie MacDonald and David McCuaig, licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0. Watch the video Precipitation Reactions starting at 6min 31sec until 9min05sec.
PreChemistry
Precipitation is one type of chemical reaction which involves the formation of one or more insoluble products. Precipitation reactions, also called double displacement reactions can be summarized with the following reaction equation: AB(aq)+CD(aq) AD(s)+ CB(aq)or(s) AB ( a q) + CD ( a q) AD ( s) + CB ( a q) o r ( s) The formation of the solid.
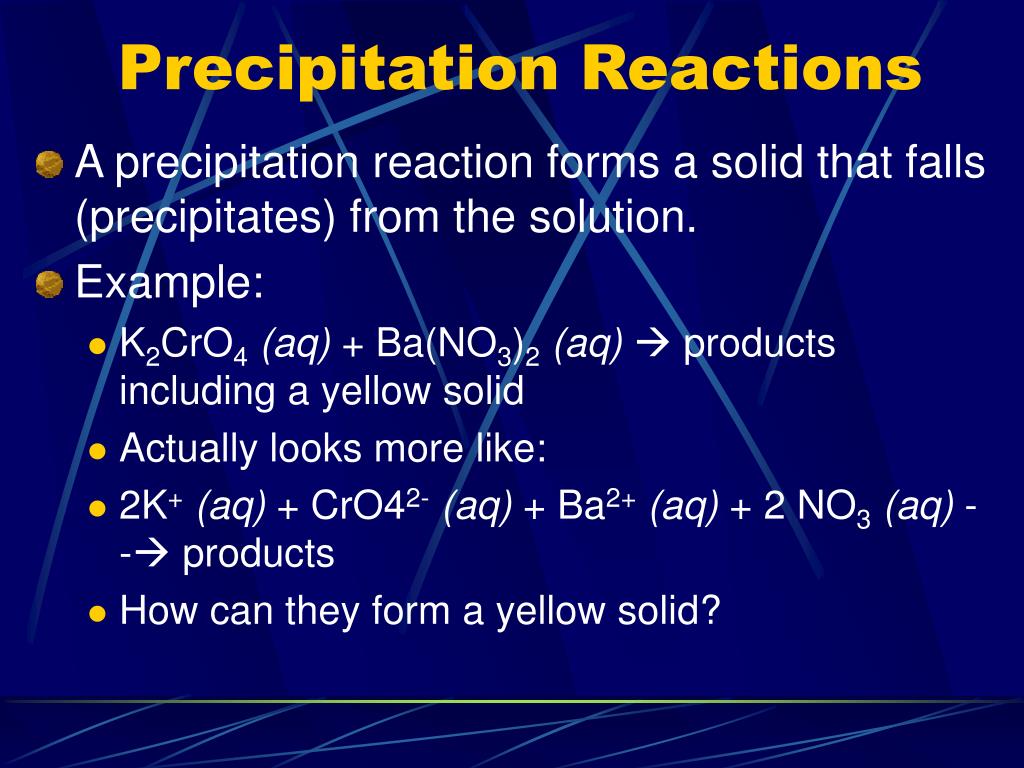
PPT Types of Chemical Reactions & Solutions PowerPoint Presentation
A comprehensive analysis of the chemical composition of precipitation was performed on rainwater samples collected between 1978 and 2017 over the conterminous US.. variance. In general, the concentration of SO 4 2− in precipitation is originated from anthropogenic sources, such as industry, fossil fuel combustion and in the case of the.

CCS Explained Carbon Capture UKCCSRC
Chemical precipitation. Chemical precipitation is the most efficient and commonly used technique to get rid of Cd +2 from the wastewater owing to its simplicity, low cost, and easy handling. In this process, chemicals react with Cd +2 forming insoluble precipitates.

chemistry Precipitation Reactions
Restrictive requirements for maximum concentrations of metals introduced into the environment lead to search for effective methods of their removal. Chemical precipitation using hydroxides or sulfides is one of the most commonly used methods for removing metals from water and wastewater. The process is simple and inexpensive. However, during metal hydroxide precipitation, large amounts of.

The general process involved in chemical precipitation [13]. Download
Before deciding whether chemical precipitation meets the needs of a municipality, it is important to understand the advantages and disadvantages of this methodology. Advantages C Chemical precipitation is a well-established technology with ready availability of equipment and many chemicals. C Some treatment chemicals, especially lime, are very.
/precipitate-589cb8953df78c47581a9014.jpg)
Precipitate Definition and Example in Chemistry
A double replacement reaction is specifically classified as a precipitation reaction when the chemical equation in question occurs in aqueous solution and one of the of the products formed is insoluble. An example of a precipitation reaction is given below: CdSO4(aq) +K2S(aq) → CdS(s) +K2SO4(aq) C d S O 4 ( a q) + K 2 S ( a q) → C d S ( s.
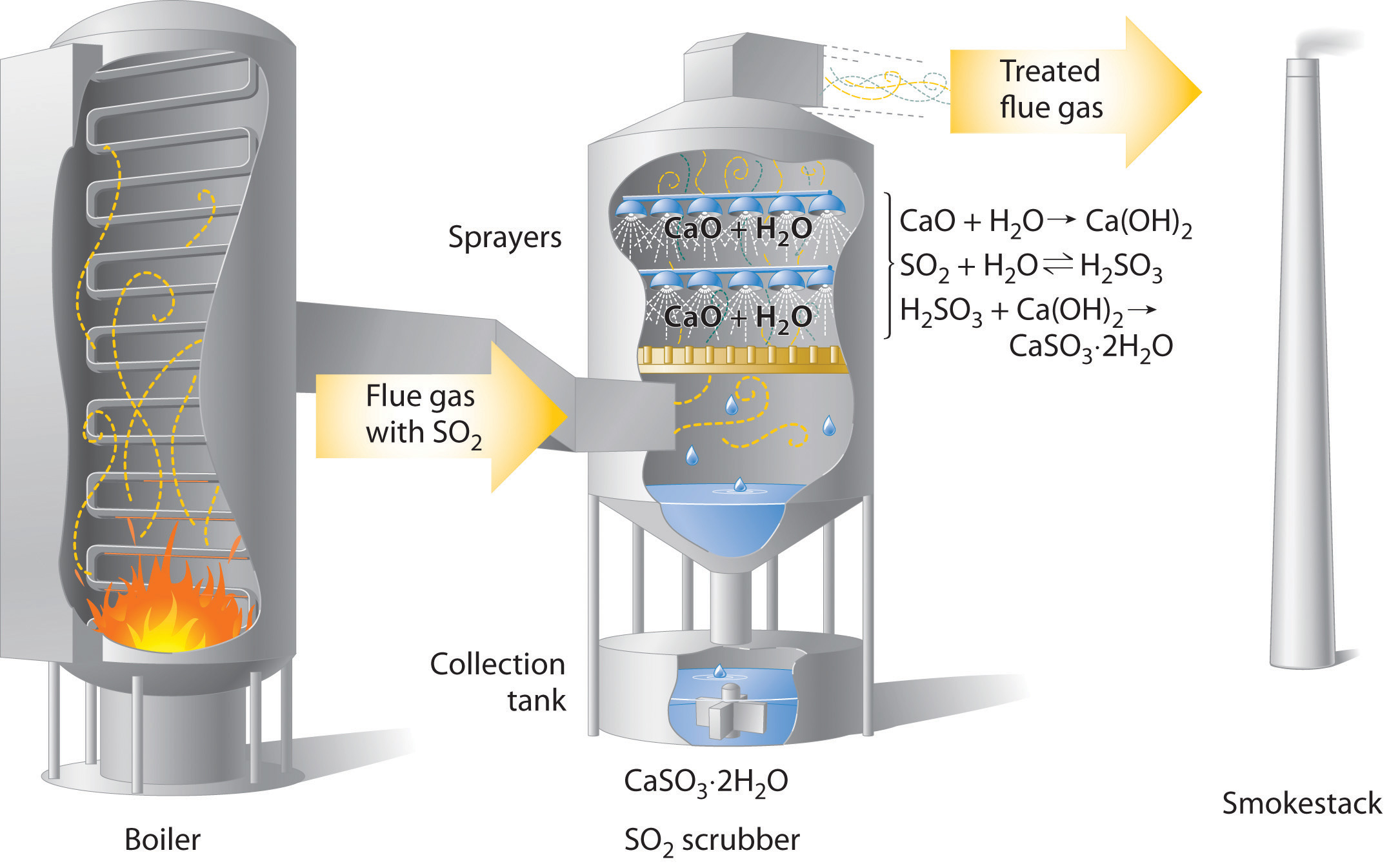
The Chemistry of Acid Rain
Deployment of carbon capture, utilisation, and storage (CCUS) technologies to mitigate climate change and overturn CO2 emissions growth would require transformational changes comprehensively. The primary focus of this manuscript is on the impurities standards and limitation that can ensure project feasibility in the long run. There is a need in the industry for guidance on purity analysis.

What are metal precipitants Netsol Water
A precipitation reaction is one in which dissolved substances react to form one (or more) solid products. Many reactions of this type involve the exchange of ions between ionic compounds in aqueous solution and are sometimes referred to as double displacement, double replacement, or metathesis reactions. These reactions are common in nature and.

Precipitation Chemistry Chemical Reaction Solution Diagram
Combustion processes proceed with chain reactions and the reaction is highly exothermic. Combined with the high-activation energy, combustion leads to large-temperature dependence. The overall reaction products can also vary (partial oxidation versus total oxidation). Partial oxidation reactions are important in chemical industry.

Precipitation Reactions Pathways to Chemistry
Power generation, natural gas processing, chemical production, hydrogen production, ethanol production, fertilizer production, and cement production are the sectors that can be specifically identified if CCUS facilities are divided based on the industry sector's maximum CO 2 capture capacity on a global scale. Other sectors of the industry are.

Precipitation Reaction a reaction that results in the formation of an
Example 6.3.1 6.3. 1: P redicting Precipitation Reactions. Predict the result of mixing reasonably concentrated solutions of the following ionic compounds. If precipitation is expected, write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction. potassium sulfate and barium nitrate. lithium chloride and silver acetate.

Processes of a conventional metals precipitation treatment plant (Wang
Water pollution by recalcitrant compounds is an increasingly important problem due to the continuous introduction of new chemicals into the environment. Choosing appropriate measures and developing successful strategies for eliminating hazardous wastewater contaminants from industrial processes is currently a primary goal. Electroplating industry wastewater involves highly toxic cyanide (CN.
- Asociacion Pequeño Accionista Valencia Cf
- Bono Alquiler Joven 2024 Andalucía
- Ampli Guitarra Valvulas Jet City
- Cubre Carter Fiat Stilo 1 9 Jtd
- Cuando Ya No Te Importa Nada En La Vida
- Busco Persona Para Limpieza De Casa
- Bachillerato Para Carnet De Conducir Camiones
- Bob Esponja Globs Of Doom Ds
- Como Cargar Una Copia De Seguridad En Whatsapp
- A Qué Hace Referencia Los Suelos De Características Especiales